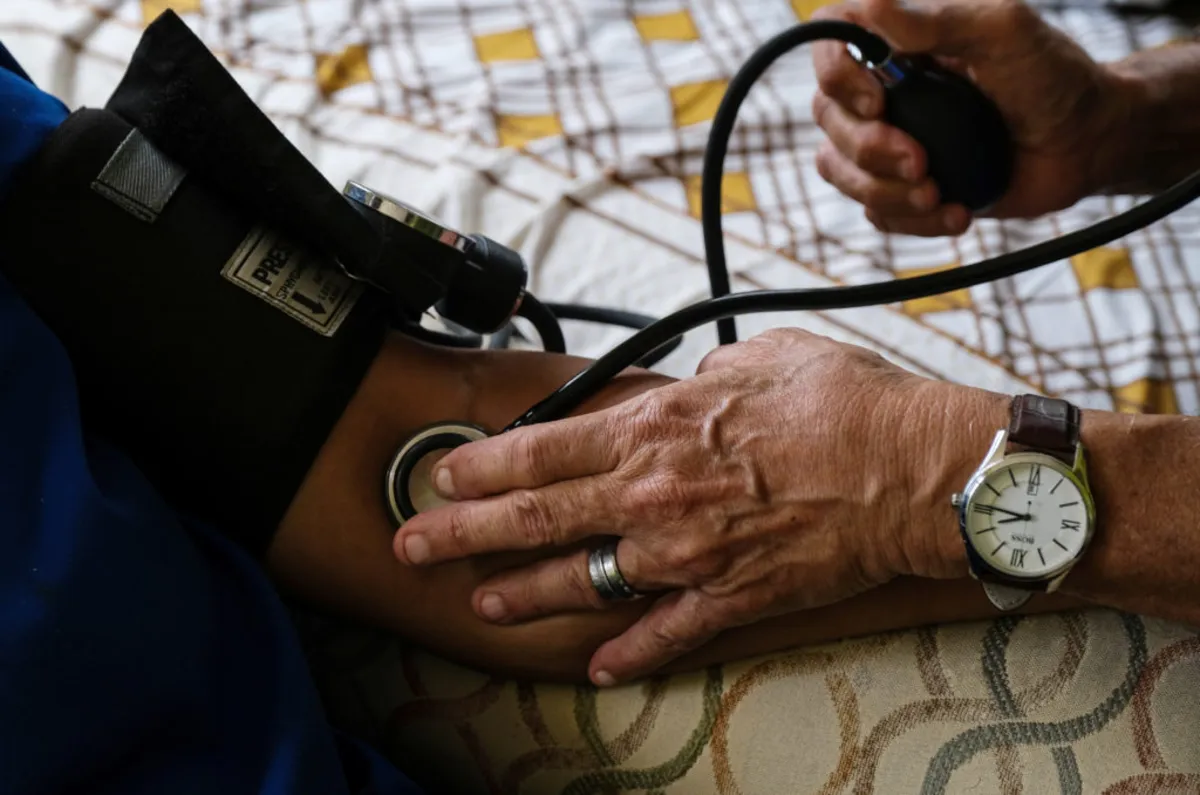
Nearly half of all Americans are affected by high blood pressure, a medical condition known as hypertension. This serious health issue is recognized as the leading risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Moreover, hypertension has been linked to an increased risk of dementia and cognitive decline. In fact, heart disease, stroke, and dementia are the first, fourth, and sixth leading causes of death in the United States. Alarmingly, only 1 in 4 individuals with a history of high blood pressure have successfully managed this condition.
In August 2025, the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology unveiled new guidelines aimed at the prevention and management of hypertension. These guidelines are based on a thorough analysis of literature published over the past decade. To shed light on the significance of these new guidelines, The Conversation U.S. consulted cardiologist Dr. William Cornwell from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
The latest guidelines introduce significant changes to the definition of hypertension. The criteria for diagnosing this condition have become stricter, leading to lower target blood pressure values compared to previous years. Hypertension is determined based on the values of systolic and diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure, represented by the top number, measures the pressure in blood vessels when the heart beats, while the diastolic pressure, indicated by the bottom number, reflects the pressure when the heart is at rest.
Notably, the new guidelines have eliminated the category of prehypertension, which was previously defined as a systolic pressure of 120-139 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure of 80-99 mm Hg. Patients are now categorized as having elevated blood pressure if their readings are between 120-129 over less than 80 mm Hg. Stage 1 hypertension is classified as 130-139/80-89, while a reading of 140/90 or more is considered stage 2 hypertension. A reading exceeding 180/120 indicates a hypertensive crisis. This change in classification may impact millions of Americans and emphasizes the importance of discussing blood pressure with healthcare providers.
The new guidelines stress the significance of lifestyle changes in managing hypertension. For instance, individuals are encouraged to seek advice from their doctors regarding dietary habits, exercise routines, and healthy sleep patterns that may help lower blood pressure. One key recommendation is to limit alcohol intake, as studies have demonstrated that alcohol consumption can elevate blood pressure. A 2023 meta-analysis indicated that systolic blood pressure increases by approximately 1 mm Hg for every 10 grams of alcohol consumed. Consequently, the guidelines suggest that men should limit their alcohol intake to no more than two drinks per day, while women should restrict themselves to one drink.
Diet plays a crucial role in controlling blood pressure. The guidelines recommend that all adults, regardless of hypertension status, consume less than 2,300 milligrams of salt daily—approximately one teaspoon—and ideally aim for less than 1,500 milligrams. In contrast, the average American consumes over 3,300 milligrams of salt per day. Patients may also explore potassium-based salt substitutes to help lower their blood pressure.
The guidelines endorse the DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) for individuals looking to prevent or manage elevated blood pressure. This diet emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, low-fat or nonfat dairy, and whole grains, which may lead to a reduction in blood pressure by up to 10 mm Hg.
Physical activity is another essential factor in managing hypertension. Research indicates that for every additional 30 minutes of aerobic exercise per week, systolic blood pressure decreases by 2 mm Hg, with the most significant reductions occurring at 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Regular physical activity not only aids in blood pressure control but also promotes longevity while decreasing the risks of heart disease, stroke, and dementia.
The new guidelines introduce the use of the PREVENT risk calculator, which incorporates various factors such as demographics, cholesterol levels, medical history, and blood pressure to assess cardiovascular disease risk. This tool is beneficial for all Americans, particularly for those with multiple chronic conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, obesity, or diabetes. The PREVENT calculator is available online, providing a reliable risk assessment for patients and healthcare providers alike.
To further reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, the American Heart Association outlines eight essential health behaviors. These include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting or avoiding smoking, ensuring adequate sleep (seven to nine hours per night), and keeping weight, cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure under control.
One of the most significant advances presented in the new guidelines is the personalized approach to hypertension management through the use of the PREVENT calculator. Healthcare providers are urged to encourage patients to monitor their blood pressure at home to gain a better understanding of daily fluctuations. Additionally, the guidelines advocate for a more aggressive treatment strategy for hypertension, recognizing that uncontrolled blood pressure poses a considerable risk for the development of heart disease and stroke.