The Sound Life study cohort comprises healthy adults aged 25 to 35 years and 55 to 65 years, who were prospectively recruited from the greater Seattle area in Washington, USA. This recruitment was conducted as part of the Sound Life Project, following a protocol (IRB19-045) approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Benaroya Research Institute. Prior to participation, all adult participants provided informed consent.
Participants were carefully screened, with exclusions for individuals with a history of chronic diseases, autoimmune diseases, severe allergies, or chronic infections. Blood samples were collected and processed into peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using a Ficoll-based approach, and all samples were frozen within 4 hours of collection. Plasma samples were also processed, aliquoted, and frozen within the same timeframe. Basic demographic information is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
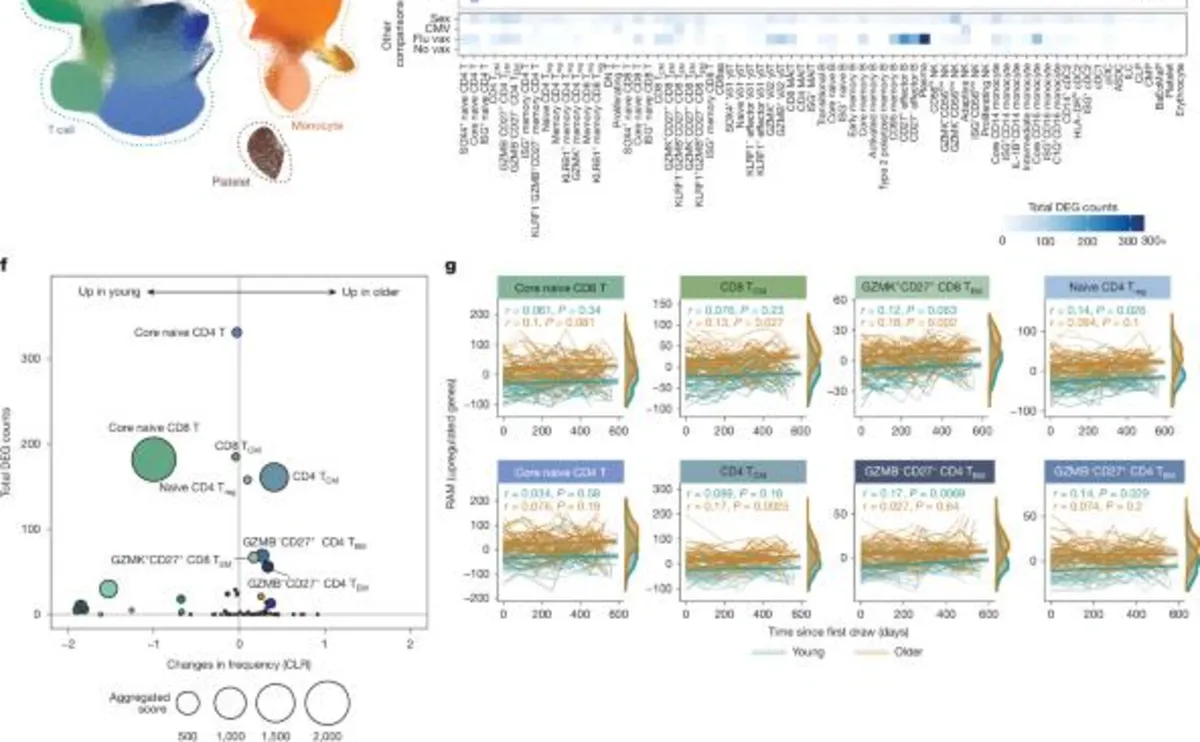
All donors received inactivated, quadrivalent influenza vaccinations corresponding to their respective flu seasons, including FLUARIX Quadrivalent for 2019-2020 and 2021-2022, and Fluzone for the 2020-2021 season. Additionally, a follow-up cohort was established under a protocol approved by the Stanford University IRB, comprising 234 paired PBMCs and serum samples from healthy adults aged 40 years and older, recruited from the greater Palo Alto area, California. Informed consent was also obtained from these participants, and their studies were approved by the Allen Institute IRB, with basic demographics provided in Supplementary Table 1.
The Olink Explore 1536 platform was utilized to measure the relative expression of 1,472 protein analytes in plasma samples from the Sound Life cohort. For the follow-up cohort, the Olink Explore 3072 platform measured the expression of 2,943 protein samples in serum. Samples were randomized across plates to ensure a balanced distribution of age and sex, with bridging controls included for cross-batch normalization.
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed on thawed PBMCs from the Sound Life cohort using the 10x Genomics Chromium 3′ v.3 chemistry. Thawed PBMCs were stained for oligonucleotide-tagged antibodies and loaded onto Chip G wells at a density of 64,000 cells. Subsequent cDNA amplification incorporated HTO additive primers. Following separation using SPRI-Select beads, library indexing reactions were conducted. For the follow-up cohort, Chromium Fixed RNA profiling was employed, with bridging controls for normalization.
Viral serology testing for human cytomegalovirus (CMV) was executed at the University of Washington’s Clinical Virology Laboratory. Plasma or serum samples were processed through the FDA-approved LIAISON CMV IgG Assay to detect CMV IgG class antibodies, with results reported as either ‘positive’ or ‘negative’ alongside a CMV antibody screen index value.
For adaptive NK cell flow cytometry, PBMCs were stained for viability, blocked, and then stained with a cocktail of surface marker antibodies. Following incubation and washing, cells were fixed and permeabilized before being incubated with an intranuclear antibody staining cocktail. Data acquisition occurred on a BD Symphony flow cytometer, with analysis conducted using BD FACSChorus software.
The Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) 96-well HAI 9-plex Assay was utilized to measure neutralizing antibodies in human plasma, blocking the binding of labeled red blood cell vesicles to trimeric influenza hemagglutinin (HA) antigens. The assay involved multiple steps, including sample dilution, incubation with HA reference standards, and reading on an MSD SECTOR S600 ECL plate reader, with results reported as a percentage of inhibition.
PBMCs were rapidly thawed and seeded for flow cytometry analysis, with a focus on characterizing B cells and measuring total influenza-specific antibody levels. The MSD Prototype Influenza 7-plex Serology Assay protocol quantified IgG antibodies in human plasma specific for various influenza vaccine HA antigens, with detailed methodology ensuring accuracy and reliability in the results.
For the analysis of cytokine production by T cells, cell supernatants were analyzed using the MSD platform, measuring several cytokines. Additional flow cytometry analyses involved traditional hierarchical gating and advanced data visualization techniques. Tools like the Human Immune Health Atlas and Dynamics of Human Immune Health and Age Resource were developed to facilitate exploration of the extensive data collected.
The Sound Life study represents a significant advancement in understanding immune health dynamics across different age groups. Through rigorous methodologies and comprehensive data analysis, findings from this study can inform future research and public health initiatives aimed at improving vaccination strategies and immune system understanding.