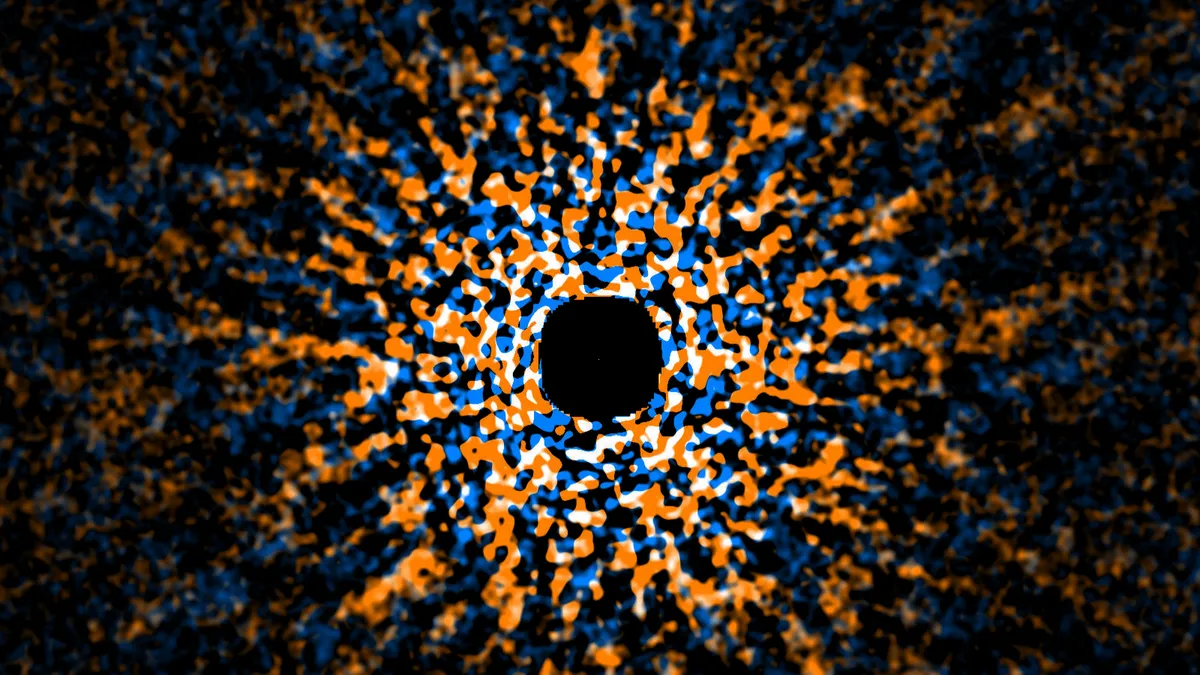
Exoplanets, defined as planets that exist beyond our solar system, are a central focus for astronomers. These distant worlds hold the key to unlocking many of the universe's mysteries, from understanding the formation of the cosmos to the possibility of extraterrestrial life. One such intriguing exoplanet is GJ 504 b, which orbits the star GJ 504 in a manner akin to how Earth orbits our sun.
GJ 504 b is an exoplanet estimated to be between three to six times more massive than Jupiter, leading some astronomers to refer to it as a "second Jupiter." This massive size makes it an interesting subject of study for researchers who are keen on understanding the diversity of planetary systems beyond our own.
The star GJ 504, around which this exoplanet orbits, is situated in the constellation Virgo, approximately 60 light-years away from Earth. GJ 504 b is located about 44 astronomical units (AU) from its star, a distance comparable to the span between the sun and Pluto in our solar system. This vast distance provides a unique perspective on how different celestial bodies can exist within their respective solar systems.
The Strategic Explorations of Exoplanets and Disks with Subaru (SEEDS) project has played a crucial role in capturing images of GJ 504 b. By utilizing a specialized coronagraph imager, researchers can observe exoplanets by filtering out the overwhelming brightness of their parent stars. This technique is essential for conducting direct observations of exoplanets like GJ 504 b, which are usually very faint and difficult to photograph directly.
Successful imaging of GJ 504 b has allowed scientists to analyze its features more accurately. Notably, researchers determined that the exoplanet has a temperature of 500 Kelvin (approximately 440.33 degrees Fahrenheit or 230 degrees Celsius), which is considered high for humans but relatively low for a planet. Furthermore, observations indicate that GJ 504 b has fewer clouds in its atmosphere compared to other known exoplanets, providing valuable insights into its atmospheric composition and weather patterns.
The study of exoplanets like GJ 504 b not only enriches our understanding of the universe but also opens up new avenues for exploring the potential for life beyond Earth. As technology advances and more exoplanets are discovered, the mysteries of our cosmos continue to unfold.