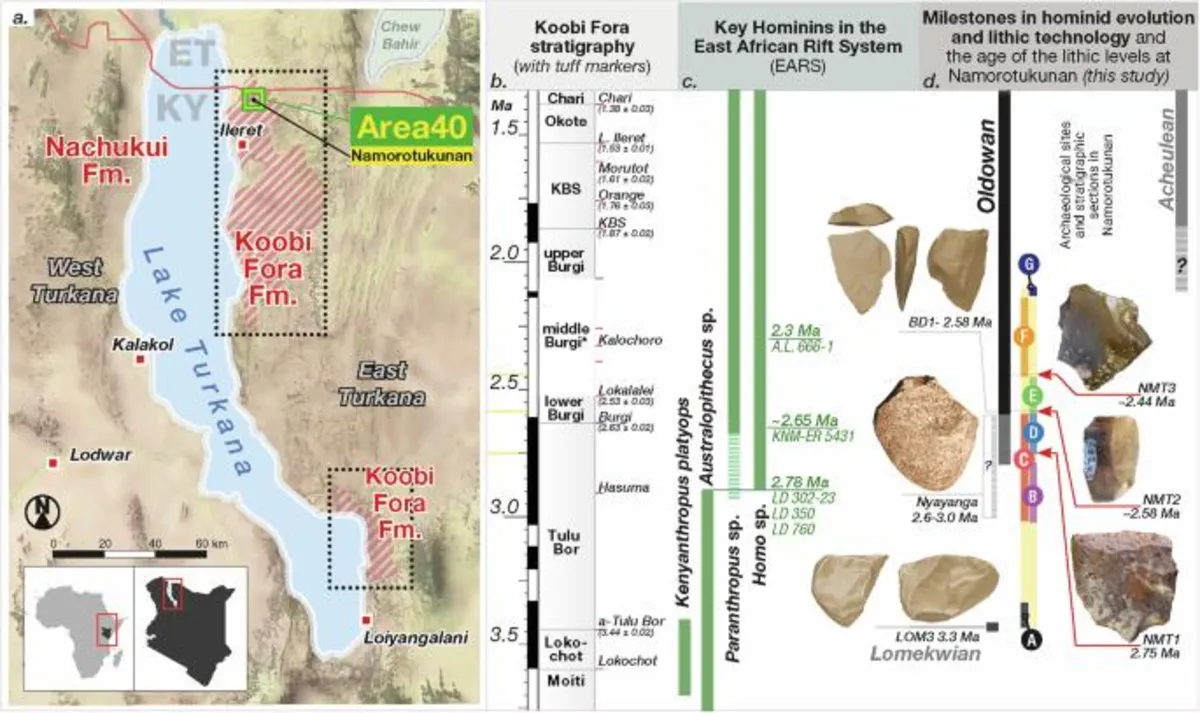
The Koobi Fora Formation (KF Fm.) represents a significant geological feature comprising sedimentary strata from the Omo Group, located on the eastern side of Lake Turkana. This formation lies unconformably atop Miocene and Pliocene volcanic rocks and associated sediments. The Omo Group includes various Plio-Pleistocene lacustrine and fluvial deposits that fill alternating half-grabens within the Omo-Turkana Basin, which is part of the broader East African Rift System (EARS).
Extensive age control within the Omo Group is achieved through 40Ar/39Ar dating of volcanic ash layers, as well as K/Ar dates from intercalated basalts and paleomagnetic stratigraphy. The KF Fm. is stratified into eight distinct members, each defined by a dated volcaniclastic tephra marker bed at the base, with the exception of the basal Lonyumon Member. In Area 40, where the Namorotukunan site is situated, sedimentary strata are estimated to span from approximately 4.3 to 1.6 Ma, interrupted by the Burgi Unconformity around 3.0 - 2.5 Ma.
Above the Burgi Unconformity, a series of lake clays suggest a local shift in tectono-sedimentary patterns, including the transgression of Paleo-Lake Lorenyang within the Turkana Basin. West of Namorotukunan, across the North Gele Fault, a younger sedimentary succession is exposed, which includes the Upper Burgi and KBS Members, as indicated by the presence of the KBS Tuff within that sequence.
Geological investigations focused on a 46-meter-thick stratigraphic interval examined across seven sections, each assigned to local geological units for mapping purposes. The lowest unit is identified as the Tulu Bor Tuff, while the uppermost unit comprises lake clays associated with the hill known as Namorotukunan, from which the archaeological site derives its name.
Archaeological research in Area 40 at the Namorotukunan site yielded a total of 1,290 artifacts from three excavation areas: Namorotukunan-1 (NMT1), Namorotukunan-2 (NMT2), and Namorotukunan-3 (NMT3). The artifacts, primarily located within sands and fine gravels, include signs of minor post-depositional disturbance as indicated by the absence of smaller artifact fractions and related linear orientations.
The lithic assemblages show evidence of anthropogenic conchoidal fractures, characterized by features such as prominent bulbs of percussion and clear striking platforms. A high proportion of sharp-edged flakes indicates the technology's focus on creating effective tools. The findings suggest a close similarity between the Namorotukunan assemblages and other early Oldowan sites, reinforcing the hypothesis of a developed understanding of fracture mechanics among the hominins of this region.
The stratigraphic sequence in Area 40 provides a framework for examining paleoecological conditions from approximately 3.44 to 2.0 million years ago. The presence of paleosols, along with associated sediments and fauna, allows for a multiproxy reconstruction of fluctuating environmental conditions during this period. Analysis of pedogenic carbonates, plant wax biomarkers, and phytoliths yields insight into the diverse habitats that existed in the late Pliocene and early Pleistocene.
Data suggest a transition from humid floodplain ecosystems, characterized by high rainfall, to more arid conditions marked by an increase in C4 vegetation and a decline in grass phytoliths. This climatic shift aligns with the onset of the gravel and paleosol interval around 2.7 - 2.2 Ma, indicating a significant reorganization of vegetative landscapes.
The archaeological findings from Namorotukunan highlight the adaptive behaviors of early hominins in response to environmental changes. The production of sharp-edged tools correlates with the need to exploit high-quality dietary resources, such as large mammalian tissues. This behavioral adaptation is thought to coincide with the emergence of early members of the genus Homo, as well as the ecological shifts across eastern Africa.
The association of hominins with favorable ecological conditions that promoted tool manufacture and burial further establishes the significance of these findings in understanding the evolution of stone tool technology in the late Pliocene. The results suggest that the Oldowan technology, evidenced at Namorotukunan, reflects an enduring adaptation to the dynamic landscapes shaped by climatic transformations.
Excavations at Namorotukunan were conducted in Area 40 from 2013 to 2022, focusing on known Early Pleistocene localities to provide a multi-disciplinary context for the lithic assemblage. All excavated materials were meticulously documented, and detailed stratigraphic information was captured using advanced mapping technologies.
Analysis of artifacts and faunal remains was carried out at the National Museums of Kenya, employing a variety of techniques to assess lithological and geochemical attributes. The use of paleomagnetic studies and geochemical methods has refined the age markers, allowing for enhanced understanding of sedimentation rates and the chronological framework of archaeological levels.