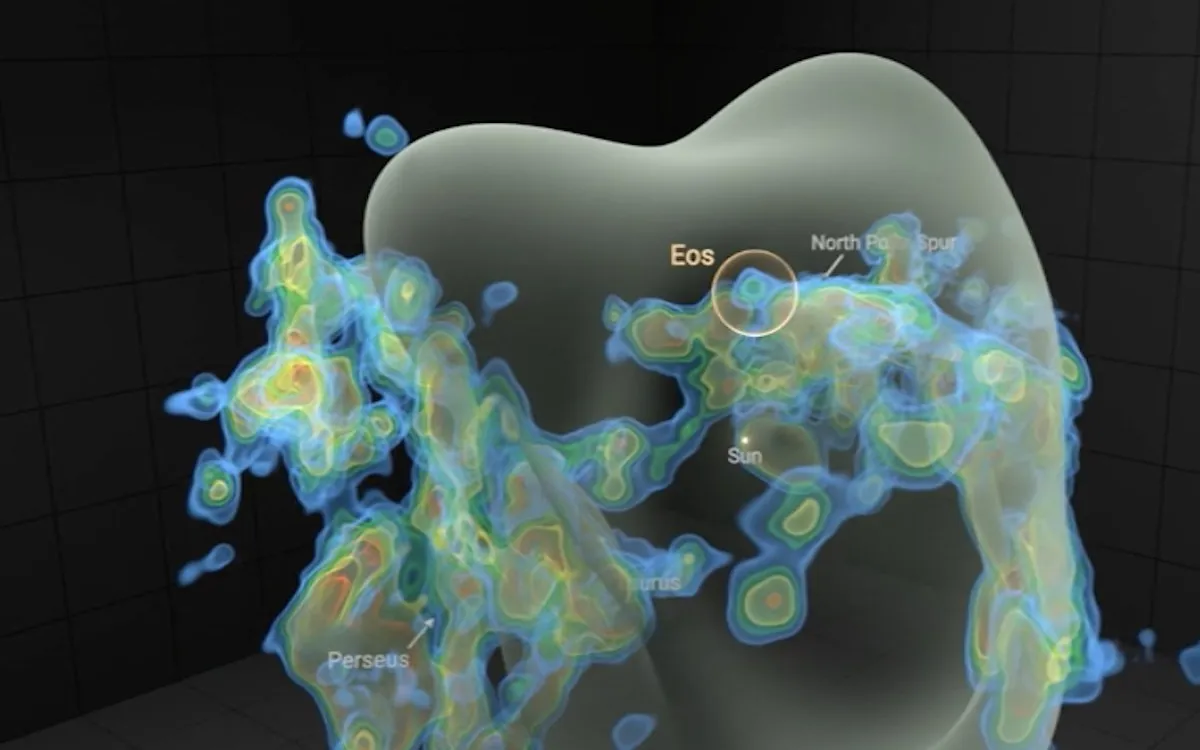
The fascinating journey of star formation begins within large, cold clouds of gas and dust, which ultimately collapse under the immense weight of gravity. These cosmic entities, known as molecular clouds, are expansive structures that can stretch for hundreds of light-years. Recently, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery of a massive molecular cloud located in close proximity to our solar system, named Eos after the Greek goddess of dawn.
The Eos cloud has been identified approximately 300 light-years away from Earth, making it one of the largest single structures visible in the sky. According to a recent study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, Eos may be the closest molecular cloud to our planet. Its proximity offers astronomers a unique opportunity to observe the intricate processes involved in star formation and to delve deeper into the mysteries of the molecular universe.
The stellar nurseries within our galactic neighborhood are situated along the surface of the Local Bubble, a vast, hot cavity filled with plasma, encased by a shell of gas and dust. To locate the molecular clouds within this bubble, scientists have primarily utilized observations of dust emissions. However, the discovery of the Eos cloud marked a significant advancement in detection methods, as researchers identified it by examining the fluorescent properties of hydrogen in the far-ultraviolet spectrum.
“This is the first-ever molecular cloud discovered by looking for far ultraviolet emission of molecular hydrogen directly,” stated Blakesley Burkhart, a physics and astronomy professor at the Rutgers School of Arts and Sciences and the lead author of the study. Molecular hydrogen, which consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded together, is the most abundant molecule in the universe. Despite its abundance, detecting it poses challenges since it emits light in far ultraviolet wavelengths that are largely absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere.
The data collected revealed glowing hydrogen molecules detected through fluorescence in the far ultraviolet spectrum. “This cloud is literally glowing in the dark,” Burkhart added, highlighting the cloud's unique characteristics. The Eos molecular cloud has a crescent shape and resides on the edge of the Local Bubble, spanning an apparent size equivalent to 40 full Moons in the night sky, with a mass approximately 3,400 times that of the Sun.
Utilizing the same innovative technique that unveiled the Eos cloud, scientists hope to discover additional hidden molecular clouds throughout the Milky Way galaxy. “When we look through our telescopes, we catch whole solar systems in the act of forming, but we don’t know in detail how that happens,” Burkhart explained. “Our discovery of Eos is exciting because we can now directly measure how molecular clouds are forming and dissociating, and how a galaxy begins to transform interstellar gas and dust into stars and planets.”