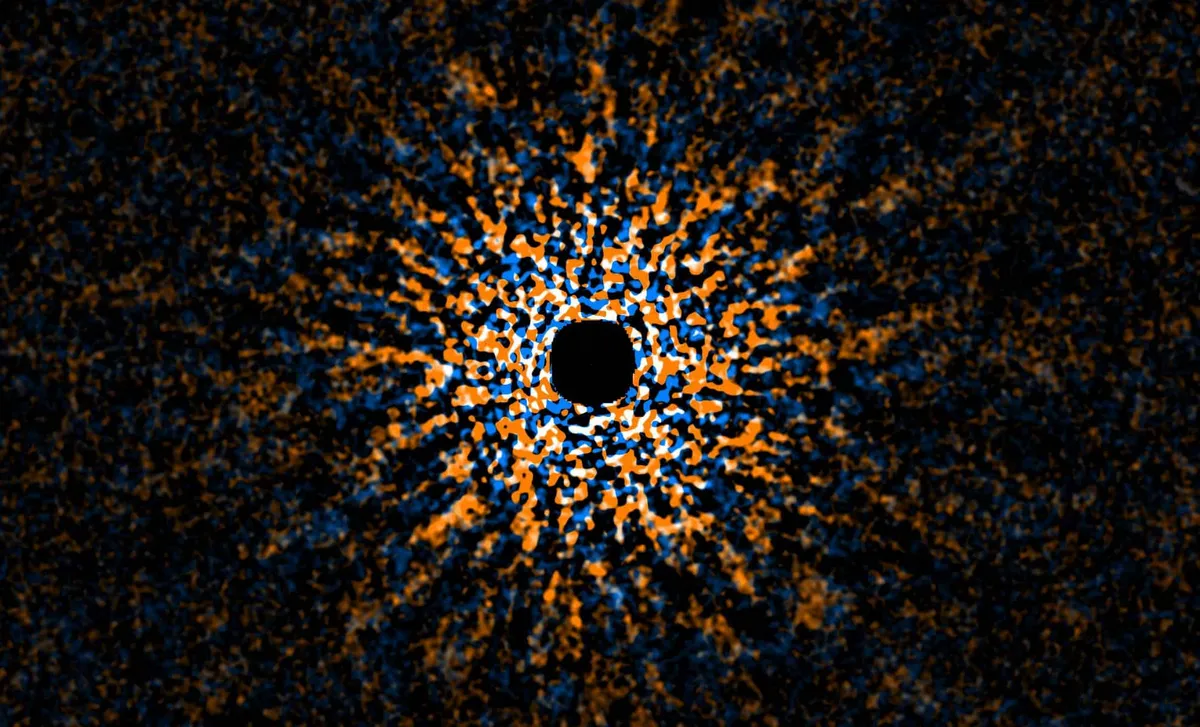
In a groundbreaking achievement, astronomers have successfully captured a direct image of GJ504b, a distant exoplanet often heralded as the “second Jupiter.” This remarkable discovery was made possible through the advanced technology of the Subaru Telescope, utilizing its state-of-the-art HiCIAO coronagraph imager alongside the AO 188 adaptive optics system. GJ504b orbits the sun-like star GJ 504, situated approximately 60 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Virgo. With an estimated mass of three to six times that of Jupiter, GJ504b has now earned the title of the lowest-mass planet ever imaged directly. This pivotal achievement marks a new era in our understanding of exoplanetary systems, showcasing the potential of sophisticated observation tools to unveil the mysteries of distant worlds.
The source of this monumental discovery can be traced back to the Strategic Explorations of Exoplanets and Disks with Subaru (SEEDS) Project. This initiative aims to delve deeper into the characteristics of exoplanets and their surrounding environments. GJ504b’s comparison to Jupiter has captivated scientists due to its striking similarities with our solar system's gas giant. Positioned 44 astronomical units (AU) from its parent star, GJ504b’s orbital distance closely resembles the gap between the Sun and Pluto in our own solar system.
Despite the similarities in size and distance to Jupiter, GJ504b offers a fascinating perspective on exoplanets, particularly regarding its composition and atmospheric characteristics. With a mass estimated to be three to six times that of Jupiter, GJ504b is among the heaviest exoplanets ever imaged. However, its faint glow and a relatively cold temperature of about 500 Kelvin (230°C) distinguish it from other exoplanets discovered thus far. The planet's relatively clear atmosphere, marked by a notable lack of cloud cover, provides scientists with an unobstructed view of its surface and atmospheric dynamics, thereby yielding critical data for future research.
Capturing direct images of exoplanets like GJ504b is an incredibly challenging endeavor. The technology employed in the Subaru Telescope’s imaging process is crucial in overcoming the significant hurdles associated with observing distant and faint celestial objects. The HiCIAO coronagraph imager plays a central role by effectively blocking out the overpowering light from the parent star, allowing astronomers to capture the faint light emitted by the planet itself. Moreover, the adaptive optics system, known as AO 188, enhances the resolution of the images by correcting distortions caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. These advanced tools empower astronomers to observe exoplanets directly and unlock essential details regarding their properties and behaviors.
The atmospheric characteristics of GJ504b offer intriguing insights into its unique environment. With a temperature hovering around 500 Kelvin (230°C), this exoplanet is relatively cold compared to many others discovered in recent years, making it a valuable subject for those interested in the diversity of planetary atmospheres. One of the most compelling aspects of GJ504b’s atmosphere is its minimal cloud cover, which sharply contrasts with numerous other exoplanets that display densely obscured atmospheres. This clarity presents a rare opportunity for scientists to explore the planet’s chemical composition and potential weather patterns in greater depth.
The discovery of GJ504b not only opens up new avenues for understanding exoplanets but also emphasizes the importance of technological advancements in astronomical research. As the SEEDS Project continues to explore exoplanets and their host stars, it plays a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of planetary formation and behavior, challenging existing paradigms and enhancing our comprehension of the universe.