The James Webb Space Telescope has made a groundbreaking discovery: it has potentially identified the first exoplanet using its advanced observational capabilities. An international team of astronomers has uncovered a planet candidate in the debris field surrounding TWA 7, a low-mass star located in the constellation Antlia, approximately 111 light-years away from Earth.
Utilizing Webb's mid-infrared instrument, the team successfully suppressed the intense glare emitted by TWA 7, allowing them to detect faint objects that would have otherwise remained hidden. This innovative technique revealed what is believed to be a previously undetected exoplanet orbiting the star, now designated as TWA 7 b.
TWA 7 b is located within the expected region for a planet of its mass, and its brightness and color align with theoretical predictions for a young, cold, Saturn-mass planet. Initial analysis suggests that this exoplanet may have a mass roughly 0.3 times that of Jupiter and a temperature around 120 degrees Fahrenheit (47 degrees Celsius), placing it well within the Goldilocks habitable range.
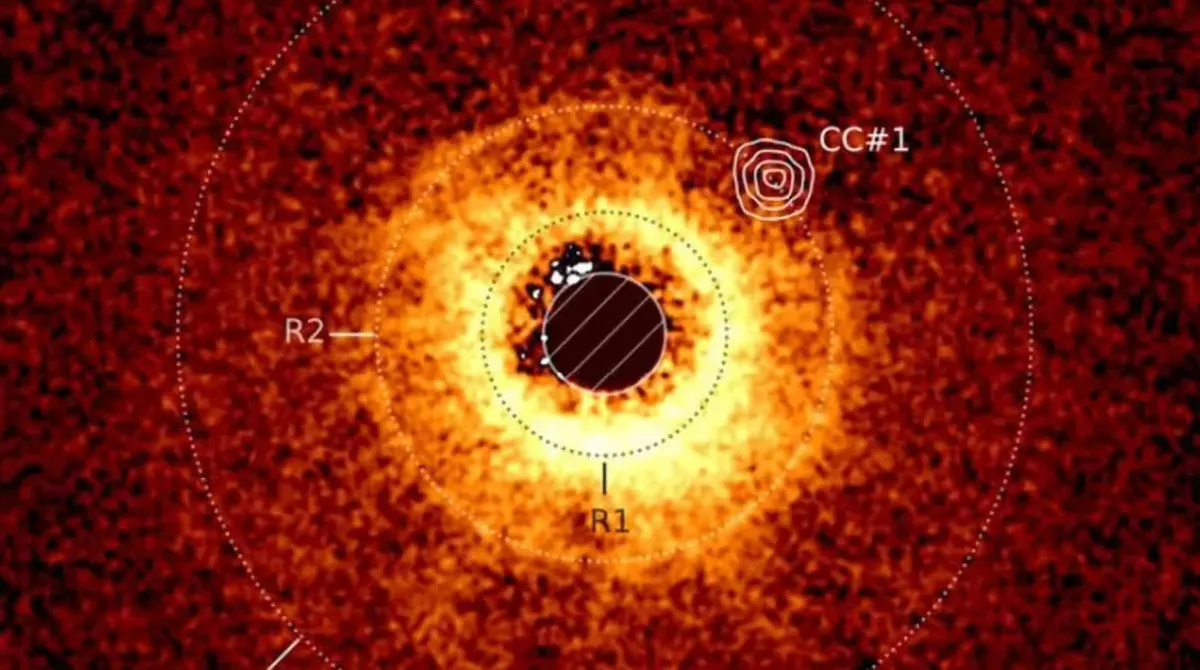
The accompanying image is a composite created using data from the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (VLT) and Webb's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). In the image, the host star TWA 7 is highlighted with a circle and a star symbol. The blue hue surrounding the star represents data from the VLT Sphere instrument, illustrating the debris field, while Webb's MIRI data is depicted in orange. The top-right orange spot indicates the new planet candidate, while another orange spot at the bottom left is likely an unrelated background star.
While it is still early in the analysis, the discovery of TWA 7 b opens new avenues for research in the field of exoplanet exploration. If confirmed, this exoplanet would mark a significant milestone as the lightest planet ever observed using this technique outside of our solar system. The distance between TWA 7 b and its host star is approximately 50 times the distance from Earth to the Sun, further emphasizing the uniqueness of this discovery.
The potential discovery of TWA 7 b by the James Webb Space Telescope demonstrates the power of modern observational technology in uncovering the mysteries of our universe. As astronomers continue their analysis, the scientific community eagerly anticipates further insights into this intriguing exoplanet and its characteristics.